网址:https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/signal/ug/autocorrelation-of-moving-average-process.html
描述:本案例由1个示例构成
-
针对以上案例,采用Python语言实现。
-
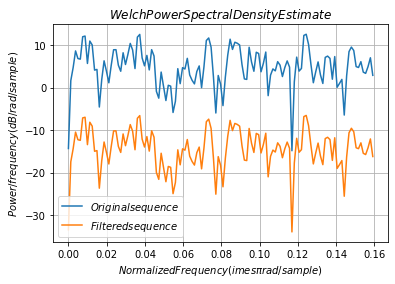
当我们在随机信号中引入自相关时,我们操纵其频率内容。移动平均滤波器衰减信号的高频分量,有效地使其平滑。 创建三点移动平均滤波器的脉冲响应。使用滤波器过滤N(0,1)个白噪声序列。将随机数生成器设置为可再现结果的默认设置。
python
from scipy import signal
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltpython
rng = np.random.default_rng()定义函数detrend
返回x:不删除趋势.
参数
----------
x : 任何对象
axis : 整数
忽略此参数
另请参见
--------
detrend_mean : 另一种detrend算法
detrend_linear : 另一种detrend算法
detrend : 所有detrend算法的包装。
python
def detrend_none(x, axis=None):
return x定义函数M_xcorr
绘制x和y之间的互相关
参数
----------
x, y : 长度为n的类数组
maxlags : 整数, 默认: 10
要显示的滞后数。如果没有,将返回 2 * len(x) - 1
滞后
Returns
-------
lags : 阵列(长度 2*maxlags+1)
滞后向量.
c : 阵列(长度 2*maxlags+1)
自相关向量
python
def M_xcorr( x, y, normed=True, detrend=detrend_none,
maxlags=20, **kwargs):
Nx = len(x)
if Nx != len(y):
raise ValueError('x and y must be equal length')
x = detrend(np.asarray(x))
y = detrend(np.asarray(y))
correls = np.correlate(x, y, mode="full")
if normed:
correls /= np.sqrt(np.dot(x, x) * np.dot(y, y))
if maxlags is None:
maxlags = Nx - 1
if maxlags >= Nx or maxlags < 1:
raise ValueError('maxlags must be None or strictly '
'positive < %d' % Nx)
lags = np.arange(-maxlags, maxlags + 1)
correls = correls[Nx - 1 - maxlags:Nx + maxlags]
return correls, lagspython
h = 1/3*np.array([1,1,1])
x = np.random.randn(1000,1)
y = signal.lfilter(h,1,x)
x = np.array(x).flatten()
y = np.array(y).flatten()
[xc,lags] = M_xcorr(y, y ,20)
Xc = np.zeros(np.size(xc))
Xc[18:23] = np.array([1, 2, 3, 2, 1])/9*np.var(x)
figure = plt.figure(111)
plt.stem(lags,xc,label = '$Sample autocorrelation$')
markerline, stemlines, baseline = plt.stem(lags,Xc,linefmt = 'r-',label = '$Theoretical autocorrelation$')
plt.setp(stemlines, 'linewidth', 2)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right")
figure = plt.figure(211)
wx, pxx= signal.welch(x)
wy, pyy = signal.welch(y)
plt.plot(wx/np.pi,20*np.log10(pxx),label = '$Original sequence$')
plt.plot(wy/np.pi,20*np.log10(pyy),label = '$Filtered sequence$')
plt.legend(loc = "lower left")
plt.xlabel('$Normalized Frequency (\times\pi rad/sample)$')
plt.ylabel('$Power/frequency (dB/rad/sample)$')
plt.title('$Welch Power Spectral Density Estimate$')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
python
